bayesNMF: Fast Bayesian Poisson NMF with Automatically Learned Rank Applied to Mutational Signatures
Citation: Jenna M. Landy, Nishanth Basava, and Giovanni Parmigiani. “bayesNMF: Fast Bayesian Poisson NMF with Automatically Learned Rank Applied to Mutational Signatures.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.18674 (2025).
R Software Package: bayesNMF
Bayesian Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) is a method of interest in fields including genomics, neuroscience, and audio and image processing. Bayesian Poisson NMF is of particular importance for counts data, for example in cancer mutational signature analysis. However, MCMC methods for Bayesian Poisson NMF require a computationally intensive augmentation. Further, identifying latent rank is necessary, but commonly used heuristic approaches are slow and potentially subjective, while methods that learn rank automatically are unable to provide posterior uncertainties. In this paper, we introduce bayesNMF, a computationally efficient Gibbs sampler for Bayesian Poisson NMF. Metropolis-Hastings steps are used to avoid augmentation, where full conditionals from a Normal-likelihood NMF is used as geometry-informed, high-overlap proposals.
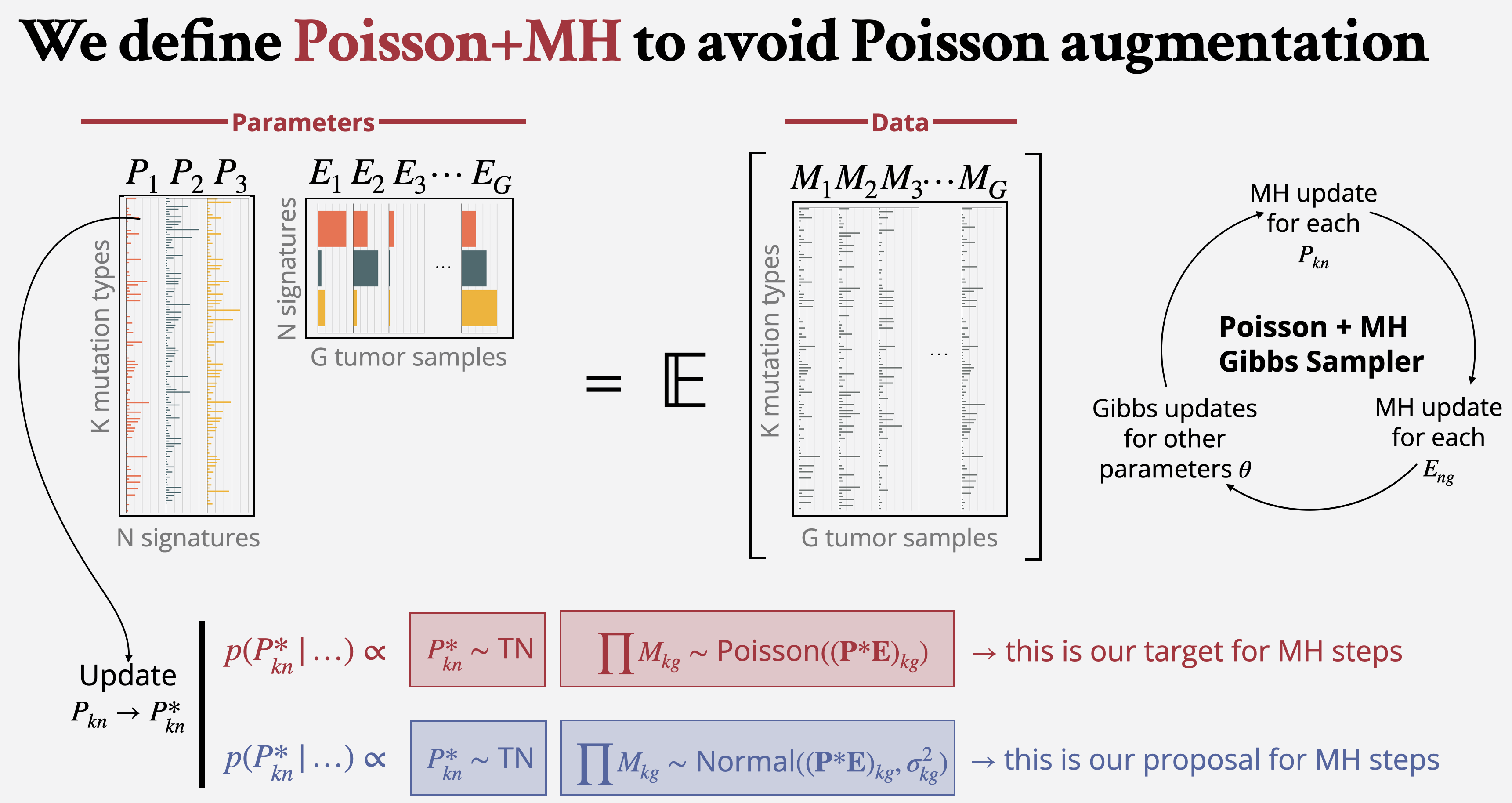
We additionally define sparse Bayesian factor inclusion (SBFI) as a method to identify rank automatically while providing posterior uncertainty quantification.
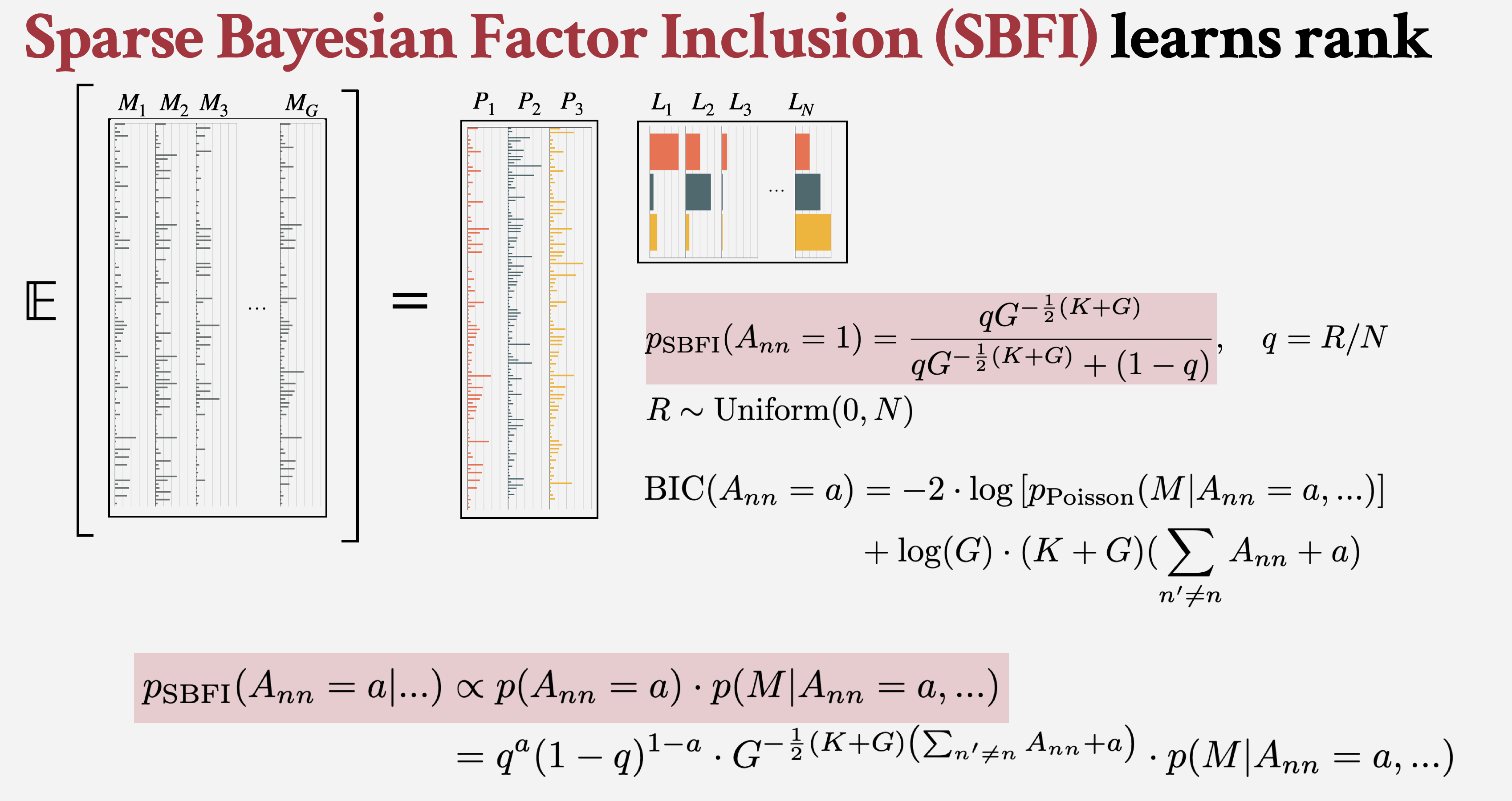 We provide an open-source R software package with all of the models and plotting capabilities demonstrated in this paper on GitHub at jennalandy/bayesNMF, and supplemental materials are available online.
We provide an open-source R software package with all of the models and plotting capabilities demonstrated in this paper on GitHub at jennalandy/bayesNMF, and supplemental materials are available online.
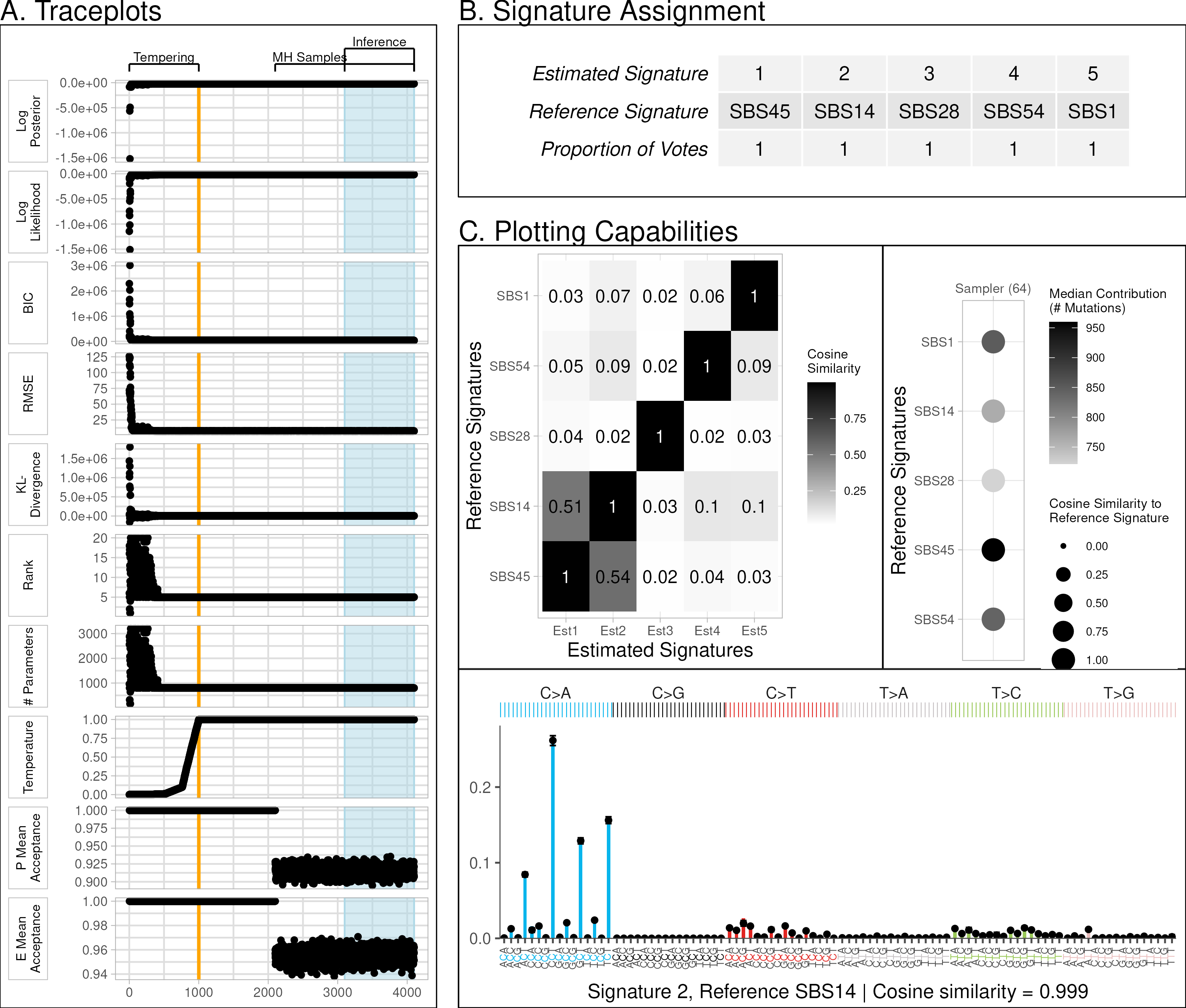
Although our applications focus on cancer mutational signatures, our software and results can be extended to any use of Bayesian Poisson NMF.
Advised by Giovanni Parmigiani, PhD
Department of Data Science, Dana Farber Cancer Institute
Department of Biostatistics, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health